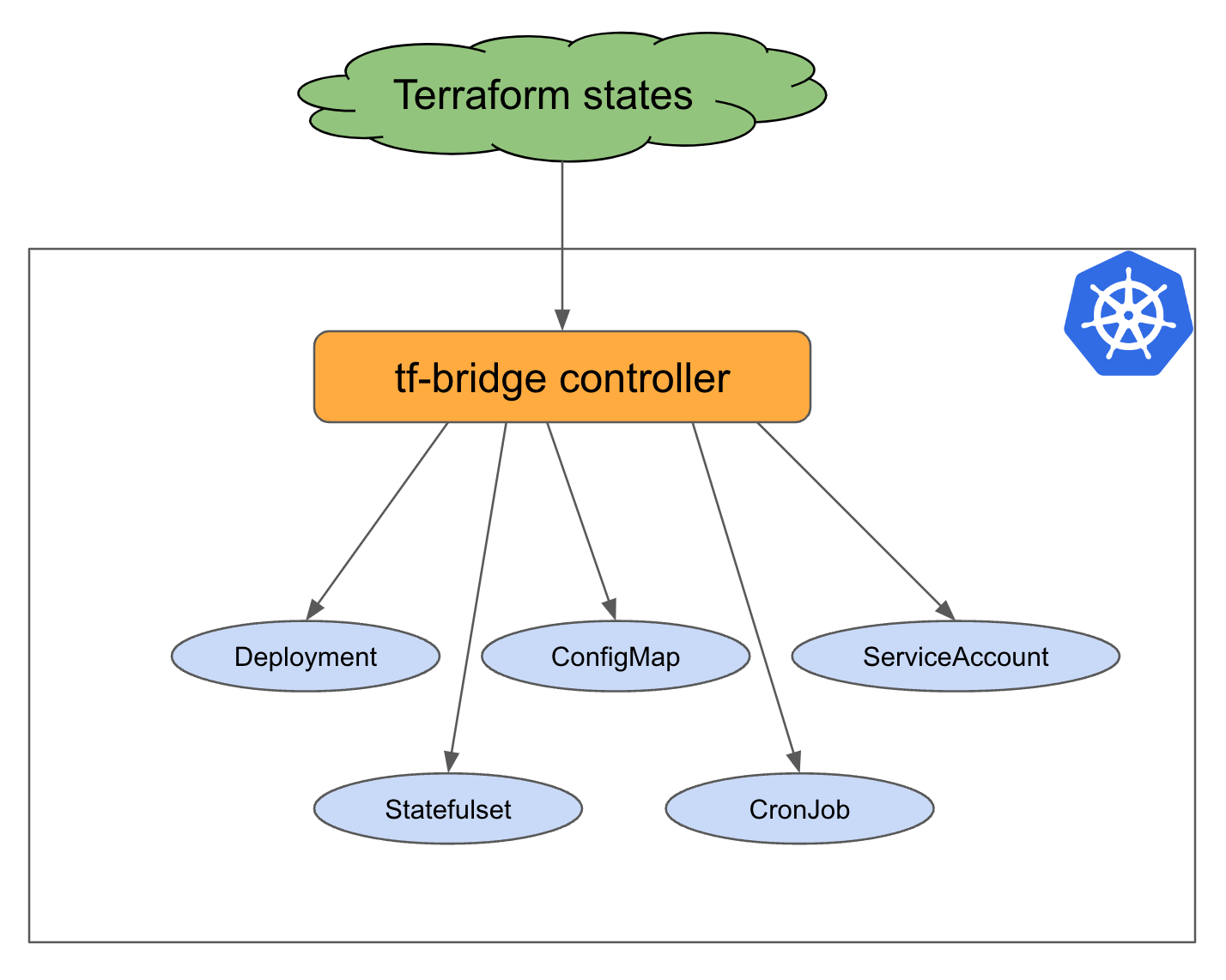
TF Bridge
A Kubernetes controller that streamlines Terraform usage along side with GitOps tools. The controller continuously monitors state produced by terraform apply and inject specified terraform outputs into the Kubernetes resources. This allows to integrate Terraform with GitOps tools like ArgoCD, FluxCD, etc.
Requirements
- A Kubernetes cluster that you can access via
kubectl - A Terraform state bucket (optional; a sample state bucket will be provided below)
- Any AWS credentials. The controller is using aws-sdk-go-v2 to access the state file in a S3 bucket in this guide, so the client requires AWS authentication. However, it doesn't matter which AWS principle it is because the file is public to all.
Install tf-bridge
kubectl apply -f https://tf-bridge-public.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/all.yaml
- ClusterBackend CRD
- ClusterTFState CRD
- TFState CRD
- tf-bridge Namespace
- tf-bridge Deployment
- tf-bridge ServiceAccount
- tf-bridge ClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding
AWS SDK Authentication
If you are NOT deploying the controller to an EKS cluster, you need to provider one of the following environment variable sets in the tf-bridge Deployment for the AWS SDK to authenticate.
They can be generated on your AWS console or with AWS CLI.
- AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY and AWS_SESSION_TOKEN or
- AWS_WEB_IDENTITY_TOKEN_FILE
Deploy resources
This section can be skipped if you configure ClusterBackend and TFState on the actual resources in your cluster.
Otherwise the next section will use resources deployed in this section.
kubectl apply -f https://tf-bridge-public.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/existing-resources.yaml
ServiceAccount and a Deployment from the nginx image for demo purposes.
Configure ClusterBackend and TFState
kubectl apply -f https://tf-bridge-public.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/resources-all.yaml
- ClusterBackend: it points to the sample bucket
tf-bridge-publicwhere there is a sample Terraform state file with some outputs. - ClusterTFState: it adds
nodeAffinityto the deploymentapi-server. - TFState: it adds the IRSA annotation to the service account
api-serverand db CName to the deployment environment variable list.
Validate the patching effects
kubectl get tfstate -A
NAMESPACE NAME BACKEND FULLYAPPLIED
default api-server-state s3 True
Reconciliation error
If you see any TFState or ClusterTFState not fully applied, you can add the following annotation to the TFState or ClusterTFState to trigger reconciliation.
kubectl annotate tfstate api-server-state sync=$(date +%s) --overwrite
kubectl annotate clustertfstate node-affinity sync=$(date +%s) --overwrite